How Decentralized Identity Work?

Decentralized identity (DID) is an emerging concept that aims to give individuals more control and ownership over their digital identities. DID allows users to create and manage their identities without relying on centralized authorities, such as governments or large corporations. Here’s an overview of how decentralized identity works, and what are decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials (VCs).
What are Identifiers?
Identifiers are unique elements that are used to identify each individual in a social setting or on apps and other services. Identifiers can be Name, name, birth date, Social Security number, tax Id numbers, and Unique Identity numbers like Aadhaar or email address to verify a person or entity. One key innovation is identifiers that are owned by the user, a user agent to manage keys associated with such identifiers, and encrypted, user-controlled data stores.
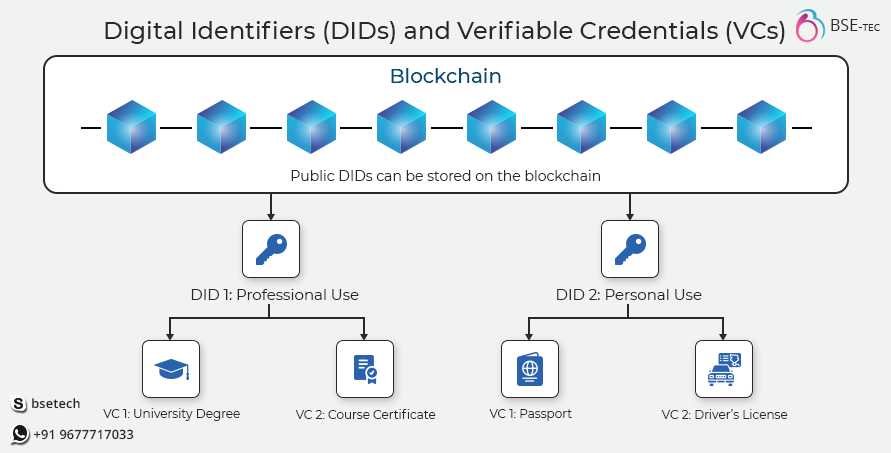
What are Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)?
Traditional identifiers like Tax id, legal name, email address, and others are legally issued by the government or other centralized entities. In such cases, the organization or government has full control over our data. But Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) are different and they aren’t controlled by centralized organizations and the user is the sole owner of their data.
What are Attestations?
An attestation is a statement that one entity makes regarding another entity. the driver’s license issued to you by the Department of Motor Vehicles (one entity) attests that you (another entity) are legally allowed to drive a car. Another example is that the university you graduated attests you with degree certificates and now you have completed a course in their institution.
What are Verifiable Credentials?
We use IDs everywhere. For example, we get driver’s licenses issued and passports issued so we can prove our identity to the officials when we land in other countries.
How Decentralized Identity Work?
The working principle of decentralized identity involves several key components and processes. In short, the DIDs are stored in a digital wallet that the user has full control over. All the documents degree certificates, driving licenses, or other things that are issued by the organizations are sent to the respective users and to an identity hub, where are all identities of users (like passports, degree certificates, driving licenses etc) are stored in a distributed ledger technology. The DIDs thus sent are stored in the user’s wallet. When they need to authenticate their identity, the required identity is verified by presenting it to the verification credentials. These VCs cross-check the presented doc in the identity hub to check if it is authentically issued by the organizations. The VCs present back the verified version to the organizations asking for authentication. Thus decentralized identity management is established without central authorities.
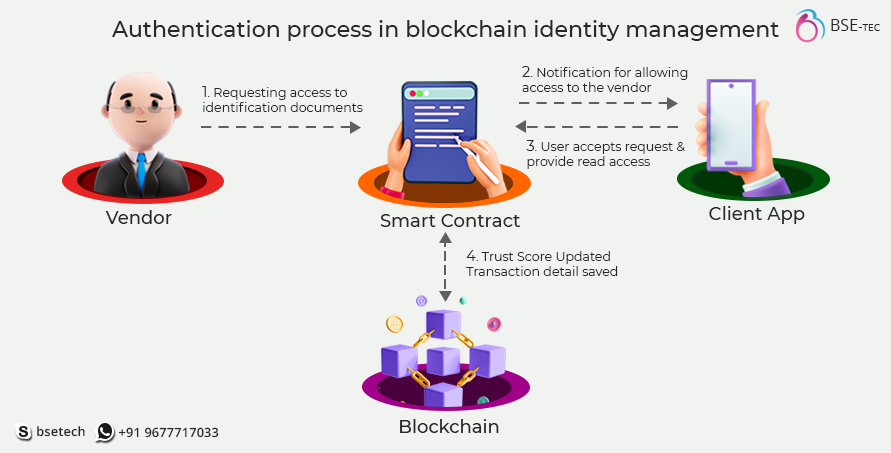
Here’s an overview of how user identity is established and managed in a decentralized identity system:
- Creation of DIDs
The first step in decentralized identity management is the creation of unique decentralized identifiers(DIDs). Users can generate their own DIDs using a decentralized identity system. DIDs are typically based on standard protocols such as W3C’s DID specification and are designed to be globally unique and resolvable across various systems and networks. DIDs can be created by individuals with the involvement of centralized authorities.
- DID Document and Key pair generation
DIDs are unique global identifiers issued to individuals, entities, and Organizations. W3C’s DID specifications are designed to be persistent and resolvable across different systems and networks.
- Issuance of Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
Verifiable Credentials (VCs) are digital representations of claims or attributes about an identity. Trusted issuers, such as governments, educational institutions, or employers, issue VCs to individuals. VCs contain the claims, are digitally signed by the issuer using their private key, and can be associated with the user’s DID.
- Storage of Decentralized Identity (DIDs)
The storage of users’ DIDs, DID documents, and Verifiable credentials (VCs) are typically stored on a decentralized and distributed ledger such as blockchain systems. Storing them in a decentralized environment enhances security, transparency, and accessibility.
- Selective Disclosure and Presentation
When interacting with service providers or relying on parties, users can selectively disclose their VCs to service providers without disclosing unnecessary personal information. Selective disclosure helps protect privacy and limits the exposure of sensitive information.
- Verification of Verifiable Credentials
Relying parties, such as service providers or verifiers, independently verify the authenticity and validity of the presented VCs. Verification involves checking the digital signature of the issuer using their public key, ensuring the integrity of the credential, and verifying that the issuer is trusted. Standardized protocols and cryptographic techniques are used to establish trust and validate the presented credentials.
Everyone has the right to have control over their identity. By creating digital identities we can create systems where users can have control over their full personal identity. By leveraging decentralized and cryptographic technologies, decentralized identity systems provide enhanced privacy, security, and user empowerment in the digital realm. Discover how this innovative technology is revolutionizing the way we manage and protect our digital identities. Looking for a blockchain development company that specializes in decentralized identity? Contact BSEtec for more information.




