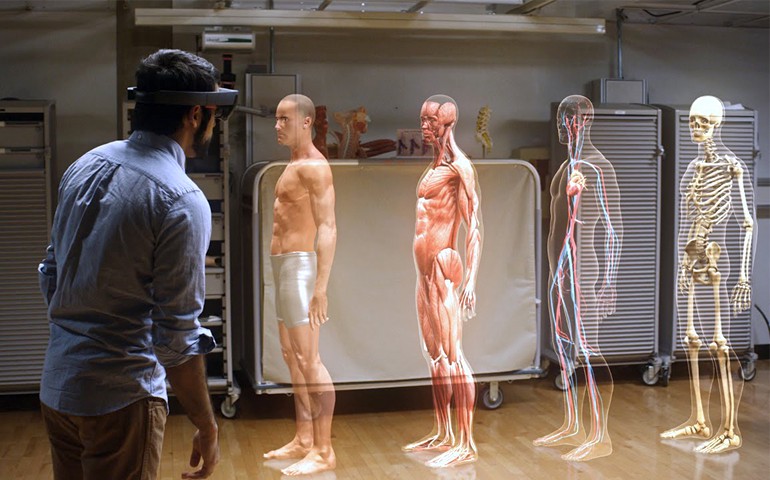
AR in Health care
Virtual reality/Augmented Reality (VR/AR) — a computer-enabled technology that simulates 3D interactive environments — is rapidly emerging as a real game changer in healthcare, where the technology is particularly well suited for quick adoption.
The range of applications for VR/AR technology in healthcare is immense. VR/AR is already being used in advanced medical training and education.
VR/AR systems enables for medical trainees to experience realistic 3D medical emergency scenarios and acquire hands-on experience with complex medical procedures without also being subjected to the risk of making errors in a real world setting.
Airline pilots train using sophisticated flight simulators, physician trainees can use VR/AR technology to practice and hone their skills at their own pace. Training tasks can be monitored and tracked to ensure competency has been reached before allowing a trainee to operate on real patients, i.e., surgical skills assessment without the traditional risks. VR/AR may enable reducing the number of cadavers needed by medical schools.
VR could be used to train to handling mass casualty scenarios or accidents in unusual industrial settings, which requires urgent and accurate triage responses.
VR is poised for continued growth across the healthcare industry in both the U.S. and emerging economies such as India and China, where rapidly expanding healthcare markets will fuel its adoption.
The worldwide market for virtual reality in healthcare is slated to reach $3.8 billion dollars by 2020 .At present virtual reality is being used to train and test surgeons ,before they actually operate on somebody. In America many Universities have begun integrating virtual reality including creating a virtual trauma bay with a 360-degree video where the viewer is in control of what is being watched, allowing them to freeze an image at any point to observe important elements in the room.
Augmented reality (AR) is a blend of virtual reality (VR) and real life. AR users are able to interact with virtual contents in the real world and to distinguish between the two.
Media outlets from the Bloomberg to Fortune have wondered if 2017 will be the year of VR/AR. From a sales perspective, there may be truth to this claim: according to Deloitte estimates, 2017 will mark the VR/AR industry’s first billion-dollar year.
Needless to say, virtual reality is having a huge moment. And while the video game industry remains the market leader, other industries — including healthcare — have also made significant strides in the VR space. In 2004, there were about 100 virtual reality-related articles on PubMed; today, there are 6,121. Until recently, virtual reality technology for medical use was primarily cultivated in academic research settings, but in the last few years, private industry interest in the technology has erupted.
According to Goldman Sachs, healthcare now represents the second largest VR/AR market, and it’s already clear how VR has changed the landscape of medicine for all stakeholders.
The Programs tend to fall under one of three larger questions:
- What new social issues arise from the use of immersive VR communication systems?
- How can VR be used as a basic research tool to study the nuances of face-to-face interaction?
- How can VR be applied to improve everyday life, such as conservation, empathy, and communications systems.