How Uber Eats Makes Money? | Sources of Revenue

Uber Eats is an online food ordering and delivery software with a tagline order food to your door! Uber Eats helps users to order their favorite food from the numerous restaurants that are listed in the area they are in or to the chosen order delivery address (which often comes with an extra distant delivery charge).
Uber Eats has generated a massive revenue amounting approximately to 11 billion USD, in spite of winding up its services in many countries. Here is the revenue growth chart of Uber Eats from Statistica.
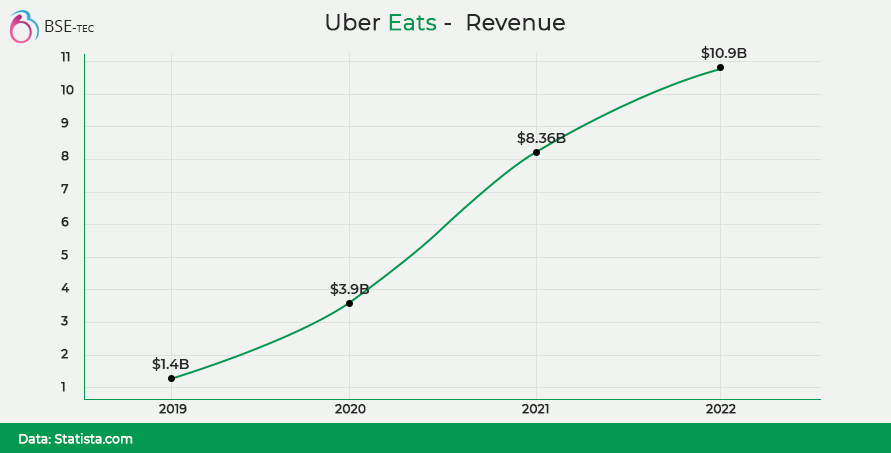
In 2019 and 2020, the service was discontinued in South Korea, India (acquired by Zomato with 9.99% for Uber), and other Eastern European nations. Additionally, it made a deal to leave Russia with the Yandex search engine. DoorDash, which overtook Grubhub to become the most popular food delivery service in 2019 in its home market, has been a powerful rival to Uber. With the $2.65 billion purchase of Postmates in July 2020, Uber strengthened its position and is going strong to date.
Uber Eats Business Model
Uber Eats operates on a commission-based business model that involves multiple stakeholders, that is, it’s a multi-sided business model. Here’s an overview of Uber Eats’ business model.
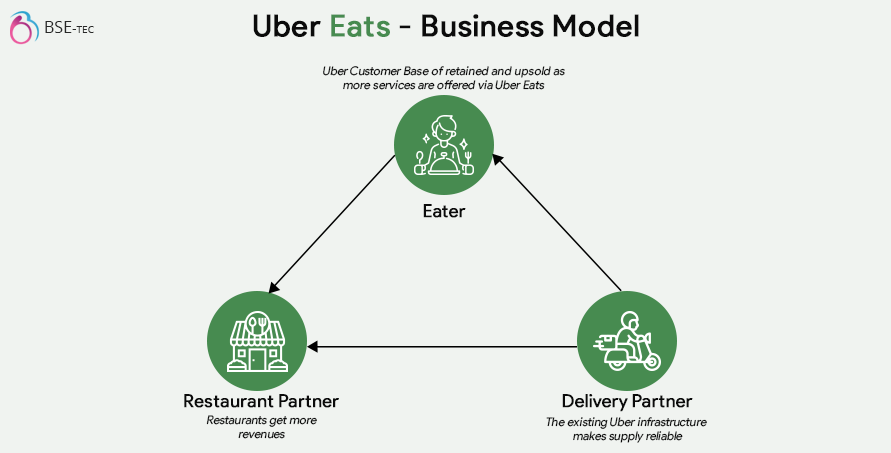
The key players in the Uber Eats business model are,
- Restaurant Partner
- Eater
- Delivery Partner
Sources of Revenue
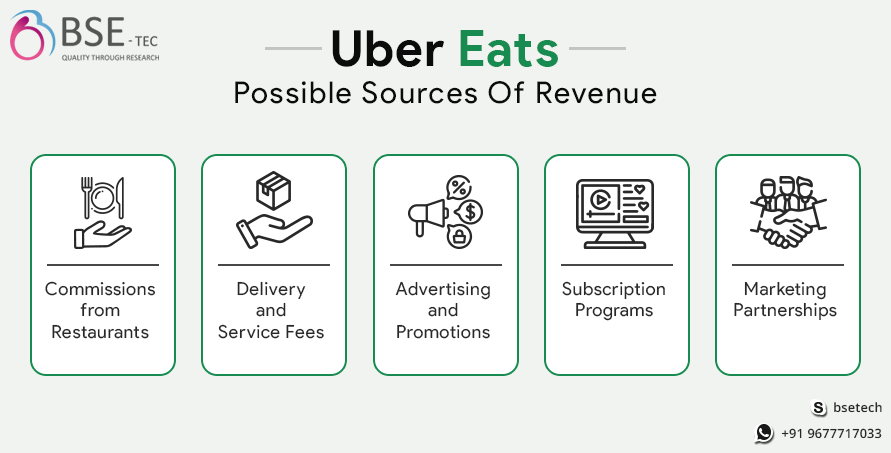
1. Commission from Restaurants: Uber Eats charges a commission fee to restaurants for each order facilitated through the platform. The commission percentage varies but is typically a percentage of the order subtotal, excluding taxes and fees. This commission covers the operational costs and services provided by Uber Eats.
2. Delivery and Service Fees: Uber Eats may charge customers a delivery fee for each order, which contributes to the revenue stream. The delivery fee amount can vary based on factors like distance, demand, and promotions.
3. Surge Pricing: During peak demand periods or in high-demand areas, Uber Eats may implement surge pricing. This means that the delivery fees and prices of certain menu items can increase temporarily to balance supply and demand.
4. Advertising and Promotions: Uber Eats offers advertising and promotional services to restaurants as an additional revenue stream. Restaurants can choose to pay for featured placements, promoted listings, or discounts to increase their visibility within the app and attract more customers.
5. Delivery Partner Earnings: Uber Eats pays a portion of the delivery fees to the delivery partners (drivers or couriers) who complete the deliveries. The specific earnings structure may vary based on factors such as distance, time, and order value.
6. Advertising or Marketing Partnerships: Uber Eats may enter into marketing partnerships with restaurants, brands, or other businesses. These partnerships can involve various forms of collaboration, such as joint promotions, sponsored events, or exclusive deals, which generate additional revenue for Uber Eats.
It’s important to note that specific commission rates, fees, and revenue-sharing models can vary based on regional markets and individual agreements between Uber Eats and its partners. The revenue generated through these various streams enables Uber Eats to cover operational costs, expand its platform, and invest in further growth and development. Hope you learned about the financial side of Uber Eats and uncovered the key sources of revenue that drive its profitability. Find out how BSEtec, can help you build a custom online food delivery app. Get in touch for a free consultation.
Did you find this article useful? Let us know by leaving a comment below, or join us on Twitter and Facebook.




